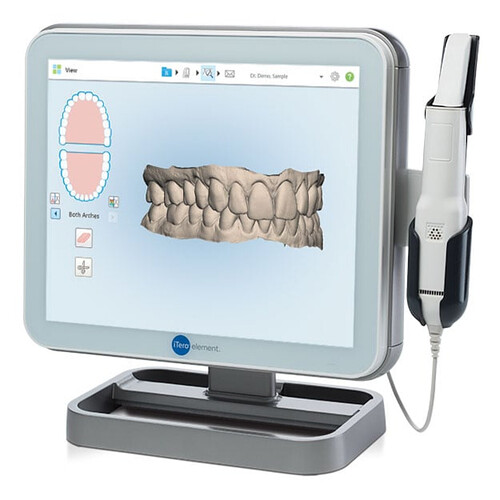
Digital scanners, also known as intraoral scanners, are advanced tools used in dentistry to capture precise, high-resolution 3D images of a patient’s teeth, gums, and oral structures. They replace conventional dental impressions, offering multiple benefits in diagnosis, treatment, and patient comfort.
Uses in Dentistry
Digital scanners are widely used across various dental specialties:
-
Restorative dentistry (crowns, bridges, veneers)
-
Orthodontics (aligners, treatment planning)
-
Implantology (guided implant surgery, implant planning)
-
Prosthodontics (dentures, prosthetic design)
-
Creating 3D models for surgical planning and diagnostics
Advantages to Diagnosis and Treatment
- Accuracy: Digital scans capture intricate details with high precision, reducing errors compared to traditional impressions, improving fit and outcomes.
- Faster turnaround: Digital data can be sent directly to labs, shortening the production time of restorations and enabling same-day procedures in some cases.
- Better record-keeping: Digital scans can be stored indefinitely without physical space constraints.
- Improved communication: Dentists and labs can collaborate more efficiently using digital models.
Advantages to Patients
- Comfort: Digital scanners avoid the discomfort, gag reflex, and mess of traditional impression trays and materials.
- Reduced chair time: Impressions are quicker to take virtually eliminating the need for retakes due to inaccuracies.
- Less anxiety and better experience: Non-invasive, clean, and fast scans enhance patient experience overall.
Disadvantages and Limitations
- Initial cost: Digital scanners can be expensive to acquire and maintain for dental practices.
- Learning curve: Requires training for dentists and assistants to operate effectively and capture quality scans.
- Data size and software dependency: Digital files are large and require compatible software and hardware for processing and storage.
- Limited use in some clinical situations: May have challenges capturing full arch scans or highly reflective surfaces without artifacts.
In summary, digital scanners in dentistry provide enhanced diagnostic and treatment capabilities while improving patient comfort and experience. However, their use requires investment, training, and careful management of digital workflows.
MBH/AB